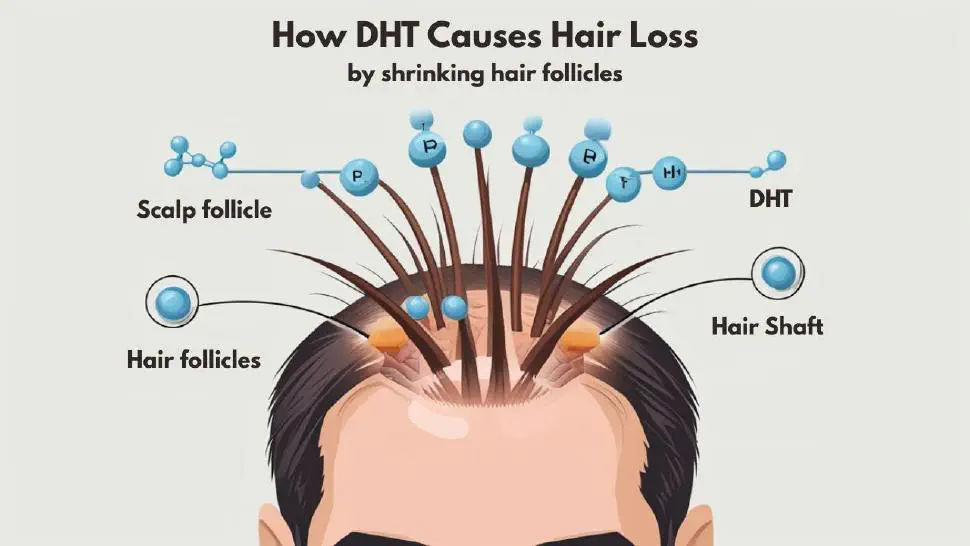
What is a natural DHT blocker?
DHT, or Dihydrotestosterone, is a hormone that is derived from testosterone through the action of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. Although it plays an essential role in the development of male characteristics during puberty, such as body hair growth and a deeper voice, DHT also binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, potentially leading to hair thinning and eventual hair loss—a condition known as androgenetic alopecia or male pattern baldness.
This process affects both men and women, although it is more prevalent in males. In hair follicles sensitive to DHT, the hormone causes them to shrink over time and produce finer and weaker hair strands until the follicles stop producing hair altogether. Understanding DHT’s influence on hair is crucial for addressing hair loss issues and identifying effective treatment strategies.
How DHT Contributes to Hair Loss?

DHT contributes to hair loss by initiating a miniaturization process in susceptible hair follicles. When DHT binds to receptors in these follicles, it interrupts the natural hair growth cycle, specifically affecting the anagen (growth) phase, shortening its duration. This results in hair follicles entering the catagen (regression) phase prematurely, reducing their size and capability to produce healthy, thick hair.
Over successive hair growth cycles, these afflicted follicles become progressively smaller, leading to thinner hair shafts, eventual hair breakage, and increased hair shedding. The growth phase shortens, while the telogen (resting) phase, where no new hair grows, lengthens. This change in the hair cycle eventually leads to noticeable thinning and bald patches in areas like the crown and hairline, which are characteristic of male and female pattern baldness.
The genetic predisposition of one’s hair follicles to DHT sensitivity is a major factor in determining the susceptibility to hair loss. Moreover, hormonal fluctuations and lifestyle factors can exacerbate these effects, making managing DHT levels a key component of hair loss prevention and treatment strategies.
Androgenetic Alopecia triggers Hair loss
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, is the most prevalent form of hair loss among adults, affecting an estimated 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States alone. While the condition is largely hereditary, its manifestation is heavily influenced by the presence and activity of DHT in the scalp.
The condition is primarily genetic, often passed down from one generation to the next through inherited DNA. Specific genes dictate follicles’ sensitivity to DHT, determining how quickly and severely hair thinning and loss occur. Researchers have identified that variations in the AR gene, which encodes the androgen receptor, can increase the susceptibility of hair follicles to DHT.
Hormonal changes throughout one’s life can further influence androgenetic alopecia. Men typically experience this hair loss pattern more visibly due to higher levels of testosterone and subsequently higher levels of DHT. However, women are not immune; hormonal shifts such as those occurring during menopause can amplify hair thinning, although it typically manifests as overall thinning rather than distinct bald patches.
Damaged hair follicles DHT
Hair growth occurs through a cycle involving growth (anagen), transition (catagen), and rest (telogen) phases. In the presence of high levels of DHT, particularly in individuals with a genetic predisposition, the anagen phase becomes progressively shorter while the telogen phase is prolonged. This imbalance leads to miniaturization of hair follicles, where thick, healthy hairs are gradually replaced by finer, shorter, and more fragile hairs. Over time, these miniaturized follicles may cease producing new hair strands altogether, resulting in noticeable thinning and eventual baldness.
Pattern baldness
Pattern baldness often runs in families, with heredity playing a significant role in its manifestation. Certain genes inherited from one’s parents increase sensitivity to DHT, making some hair follicles more prone to its effects. Research has identified multiple genetic loci associated with increased risk, including the androgen receptor (AR) gene on the X chromosome, highlighting the complexity of its hereditary nature. This genetic component suggests that individuals with a family history of the condition are more likely to experience pattern baldness themselves.
Mechanism of Natural DHT Blockers
How Natural DHT Blockers Work
Natural DHT blockers operate by inhibiting the activity of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. By reducing the production of DHT, these natural substances help mitigate its adverse effects on the hair follicles, such as the shortening of the anagen phase and the miniaturization of follicles.
Key Natural DHT Blockers

1. Saw Palmetto
Saw palmetto is one of the most well-known natural DHT inhibitors. Extracted from the fruit of the Serenoa repens plant, it is believed to block 5-alpha reductase activity, thereby reducing DHT levels. Saw palmetto is often found in herbal supplements targeted towards improving hair health.
2. Pumpkin Seed Oil
Rich in phytosterols, pumpkin seed oil has shown potential in decreasing DHT. These plant-based compounds may inhibit the conversion process of testosterone to DHT, consequently reducing hair follicle damage.
3. Green Tea
Green tea contains polyphenols, particularly epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), which have been shown to reduce DHT production. The antioxidant properties of EGCG also help combat oxidative stress, providing a dual benefit for hair
4. Turmeric
Curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, is renowned for its anti-inflammatory benefits. It has been suggested to inhibit the activity of 5-alpha-reductase, thereby potentially reducing DHT levels. Adding turmeric to your meals not only enhances flavor but also may contribute to healthier hair processes.
5. Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds such as almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds provide an abundance of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for maintaining healthy hair. They are also rich in lignans and phytosterols, compounds that have been studied for their ability to block DHT production.
6. Soybeans
Soybeans and soy products contain isoflavones, primarily genistein, which have been studied for their role in modulating hormonal activity. These compounds may help regulate the levels of DHT, contributing to the mitigation of its effects on hair growth.
Comparison with Pharmaceutical DHT Blockers
At the time of hair loss treatment, particularly for androgenetic alopecia, dihydrotestosterone (DHT) blockers are a crucial component. DHT, a derivative of testosterone, is known to contribute to hair follicle miniaturization, leading to thinning hair and eventual hair loss. As such, reducing its effects is a key strategy in hair preservation. Among the available treatments, both pharmaceutical DHT blockers and natural alternatives have carved out significant roles. Understanding their differences, effectiveness, and safety profiles can aid individuals in making informed choices.
Pharmaceutical DHT Blockers
Pharmaceutical DHT blockers, primarily finasteride (Propecia) and dutasteride (Avodart), are well-established treatments usually prescribed for male pattern baldness. These medications belong to a class of drugs known as 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. Finasteride specifically inhibits the Type II 5-alpha reductase enzyme, reducing DHT levels in the scalp by about 60%. Dutasteride, on the other hand, is a more potent inhibitor, affecting both Type I and Type II 5-alpha reductase enzymes, thereby lowering DHT levels even further. These drugs have been rigorously tested in various clinical trials, demonstrating efficacy in slowing hair loss and, in some cases, promoting regrowth.
Natural DHT Blockers
Natural DHT blockers utilize herbal and plant-based ingredients believed to reduce DHT levels or balance its effects without the need for a prescription. Common ingredients include saw palmetto, pumpkin seed oil, green tea extract, and nettle root. While these natural options are accessible and generally pose fewer risks of side effects, their efficacy is often anecdotal, and supporting scientific evidence is limited compared to their pharmaceutical counterparts.
Comparing Efficacy
Pharmaceutical DHT blockers have a robust body of research backing their efficacy. Numerous studies have confirmed their ability to halt hair loss progression and, in some cases, facilitate the regrowth of hair. However, they require a prescription and come with potential side effects, including sexual dysfunction, mood changes, and impacts on prostate-specific antigen levels.
Natural DHT blockers, while popular for their perceived safety, do not have the same level of scientific validation. Some users report subjective improvements in hair thickness and reduced shedding, but these results are less predictable and vary widely among individuals.
Safety and Side Effects
Safety is a prime consideration when comparing these treatments. Pharmaceutical DHT blockers, while effective, are sometimes met with adverse effects. Finasteride, for example, has been associated with decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and depression in a subset of users. Dutasteride shares similar risks and is generally reserved for more severe cases due to its stronger action.
Conversely, natural DHT blockers are touted for their minimal side effects. Their appeal lies in their more holistic approach, often integrating vitamins and minerals beneficial to overall hair health. However, individuals with allergies or sensitivities to specific plant extracts should exercise caution, and it’s still wise to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
Benefits of Using Natural DHT Blockers
Promoting Hair Growth
Hair growth can be a complex process influenced by a multitude of factors, including genetics, hormonal balance, diet, and lifestyle choices. However, with the growing interest in natural and holistic approaches to health, many individuals are seeking sustainable ways to promote hair growth without relying solely on chemical or invasive treatments. This section explores various methods and practices that can aid in fostering healthier, fuller hair.
Nutrition and Diet
A balanced diet is fundamental for overall health and is particularly crucial for hair growth. Hair is primarily made up of a protein called keratin, so ensuring an adequate intake of protein-rich foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes can support hair structure and growth. Additionally, vitamins and minerals like biotin (vitamin B7), vitamin D, zinc, and iron are essential in minimizing hair loss and promoting new growth. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts can provide these critical nutrients.
Scalp Health
A healthy scalp is the foundation for hair growth. Regular cleansing to remove buildup and exfoliating to eliminate dead skin cells can prevent clogged follicles and create an optimal environment for hair to grow. Massaging the scalp can also improve circulation, boosting blood flow to the hair follicles, which may enhance growth. Natural oils such as coconut oil, jojoba oil, and castor oil can be used to moisturize the scalp and strengthen hair strands.
Stress Management
Chronic stress has been linked to various health concerns, including hair loss. Conditions such as telogen effluvium, where hair falls out after a stressful event, underscore the impact stress can have on hair growth cycles. Incorporating stress-reducing practices such as yoga, meditation, or even daily leisure activities can be beneficial. Moreover, getting adequate sleep is crucial, as restorative sleep can support the body’s regenerative processes, including hair growth.
Natural Supplements
For those looking to enhance their hair care routine, natural ingredients can provide an additional boost. Fish oil, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, is known for promoting hair thickness and reducing inflammation around hair follicles. Herbal supplements like saw palmetto have been suggested to support hair growth by blocking certain hormonal pathways that can lead to hair thinning. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement to ensure it aligns with individual health needs.
Avoiding Hair Damage
Maintaining hair health depends equally on what you exclude as well as what you include. Limiting the use of heat styling tools, harsh chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles that put strain on hair can prevent damage and breakage. Instead, opting for gentle hair care practices, like using a wide-toothed comb on wet hair, air drying instead of blow drying, and using protective hairstyles can preserve hair integrity. Then you don’t need any treatment for hair loss.
Minimal Side Effects
In the time of pharmaceuticals and medical treatments, the quest for efficacy often carries the burden of adverse reactions. However, a wave of innovation and research in recent years has shifted focus towards developing therapies that not only deliver powerful benefits but also maintain a minimal side effect profile. The concept of “minimal side effects” is becoming a pivotal criterion for new treatment modalities, ensuring patient adherence, comfort, and overall health.
The Science Behind Minimal Side Effects
At the core of minimizing side effects is a deep understanding of the biological mechanisms of disease and the human body’s complex systems. Advances in biotechnology and molecular biology enable scientists to design drugs with greater precision, honing in on specific targets within the body. Rather than utilizing a one-size-fits-all approach, these treatments are engineered to interact only with the disease-causing agents, thus sparing healthy cells and tissues from unnecessary exposure.
Moreover, personalized medicine is playing a crucial role in this field. By analyzing genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, medical professionals can tailor treatments that align with an individual’s unique biological makeup. This personalized approach not only enhances therapeutic effectiveness but also significantly reduces the risk of adverse effects, as treatments are customized to the patient’s own biology.
How to Incorporate Natural DHT Blockers into Your Routine
Supplements and Topical Applications
In the quest for optimal health, beauty, and wellness, many individuals turn to supplements and topical treatments as accessible avenues for enhancing their daily routines.
Nutritional Supplements: Beyond the Basics
Nutritional supplements have gained widespread popularity, serving as convenient sources of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients that may be lacking in modern diets. As lifestyles become more fast-paced and dietary habits diversified, supplements provide a valuable means of ensuring adequate nutrient intake. For instance, Vitamin D and Calcium are crucial in maintaining bone health, whereas Omega-3 fatty acids, often sourced from fish oil, are celebrated for supporting cardiovascular health.
Topical Applications: Direct Benefits to the Surface
While nutritional supplements work from the inside out, topical applications deliver active ingredients directly to the skin, hair, or nails. This direct approach allows for targeted treatment of specific concerns, from hydrating dry skin and treating acne to promoting hair growth and strengthening nails. The skincare industry, in particular, has seen a surge in products boasting potent active ingredients such as hyaluronic acid for hydration, retinoids for anti-aging, and niacinamide for brightening and soothing benefits.
Synergistic Approach: Combining Supplements and Topicals
Recognizing the potential of addressing health and beauty both internally and externally, individuals increasingly adopt a synergistic approach by combining supplements with topical applications. This integrated strategy can enhance the effectiveness of treatments, providing a more holistic path to achieving specific wellness goals. For instance, pairing oral Vitamin C supplements with a topical vitamin C serum can enhance skin radiance and protection against environmental stressors.
Ultimately, the key to maximizing the benefits of supplements and topical applications lies in selecting quality products backed by scientific evidence and tailored to individual needs. Consulting with healthcare professionals and conducting thorough research are essential steps in creating a sustainable and effective health and beauty regimen.
Dietary Changes

Increase Consumption of Green Tea: Green tea contains catechins, specifically EGCG, which are known to inhibit the conversion of testosterone to DHT.
Incorporate More Soy Products: Soy isoflavones, such as genistein, have been shown to reduce DHT levels in the body by inhibiting 5-alpha reductase, the enzyme responsible for DHT production.
Add Pumpkin Seed Oil: Rich in phytosterols, pumpkin seed oil can help lower DHT levels by inhibiting the 5-alpha reductase enzyme.
Eat More Zinc-Rich Foods: Zinc is essential for maintaining hormonal balance and can help reduce DHT production. Foods high in zinc include oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds.
Consume Flaxseeds and Flaxseed Oil: These are high in lignans, which can naturally reduce DHT levels by blocking the production and metabolism of DHT.
Include More Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds contain L-lysine, which might help inhibit DHT production and support hair health.
Focus on a High-Antioxidant Diet: Foods like berries, nuts, and dark leafy greens are high in antioxidants, which can help combat oxidative stress that might contribute to increased DHT levels.
Incorporate Turmeric in Your Diet: Curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, has been suggested to have DHT-blocking properties.
Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining overall health and can support the body’s natural regulation of hormone levels, including DHT.
Monitor Intake of High-Refined Sugars and Simple Carbs: These can cause spikes in insulin, indirectly increasing DHT production, so aim to reduce processed foods and sugars.
Evidence and Research on Natural DHT Blockers
Scientific Studies and Findings
Overview of DHT (Dihydrotestosterone) and its role in hair loss.
Examination of various natural substances, such as saw palmetto, pumpkin seed oil, and green tea, that have been studied for their DHT-blocking properties.
Analysis of clinical trials and research studies evaluating the efficacy of natural DHT blockers in reducing hair loss and promoting regrowth.
Discussion of the methodologies used in studies, including sample size, duration, and control measures.
Summary of key findings, highlighting substances with the most significant impact on DHT reduction and hair health.
Understanding Limitations and Continuing Research
Identification and explanation of common limitations in studies on natural DHT blockers, such as small sample sizes and short study durations.
Discussion on the variability in individual responses to natural DHT blockers and external factors affecting results.
Consideration of potential biases in industry-funded research and the need for independent, peer-reviewed studies.
Acknowledgment of the scarcity of large-scale, long-term studies assessing the efficacy and safety of natural DHT blockers.
Myths and Misconceptions
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a hormone that has garnered significant attention in the context of hair loss and androgenetic alopecia. As a result, DHT blockers have emerged as a popular solution for those seeking to combat hair loss. However, like many medical and health-related topics, discussions around DHT blockers are rife with myths and misconceptions. Clarifying these misunderstandings is crucial for individuals considering this route in their hair care regimen.
Myth 1: DHT Blockers Cause Impotence
One of the most pervasive myths surrounding DHT blockers is that they invariably cause impotence or erectile dysfunction. While it is true that some individuals may experience sexual side effects from DHT-blocking medications like finasteride, these cases are relatively rare. The incidence of such side effects is low, and for many people, they are often reversible upon discontinuation of the drug. It’s important to approach this topic with a balanced perspective and to discuss potential side effects with healthcare professionals.
Myth 2: Natural DHT Blockers Are Ineffective
There is a widespread belief that only pharmaceutical DHT blockers are effective, and natural alternatives are merely folklore with no scientific backing. However, certain natural substances, such as saw palmetto, pumpkin seed oil, and green tea extract, have shown promise in studies for reducing DHT levels and supporting hair health. While these natural options may not be as potent as prescription medications, they can be part of a holistic approach to hair loss prevention, especially for those wary of pharmaceutical treatments.
Myth 3: DHT Blockers Will Work Immediately
Another common misconception is that DHT blockers will produce instant results. Some individuals may expect to see noticeable changes within days or weeks of starting treatment. In reality, hair growth is a slow process, and it can take several months to see significant improvement. Patience and a consistent approach to treatment are necessary for evaluating the effectiveness of DHT blockers. Results can vary based on individual factors such as the severity of hair loss, underlying health conditions, and adherence to treatment.
Myth 4: DHT Blockers Are Only for Men
Given that men are predominantly affected by androgenetic alopecia, a myth has developed that DHT blockers are only suitable for male use. In truth, women can also suffer from hair loss related to DHT, and there are DHT-blocking treatments available that are suitable for women. Women’s hair loss patterns and causes can be different, so treatments may vary, but options are available for both genders.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Importance of Professional Guidance
When it comes to managing health concerns, particularly those involving hormonal imbalances like excess dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the importance of consulting a healthcare professional cannot be overstated. DHT plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, and its overproduction can lead to health issues including hair loss, acne, and, in some cases, prostate enlargement. Navigating the complexities of hormone regulation requires not only an understanding of these biological processes but also awareness of how they interact with overall health. Professional guidance provides the tailored insights necessary to approach these challenges effectively and safely.
Healthcare professionals, such as doctors and endocrinologists, possess the knowledge and experience to assess individual health needs. They can run diagnostic tests to determine DHT levels and evaluate the extent to which they might be impacting your health. This initial diagnostic phase is critical; it ensures that any intervention is based on accurate, personalized data rather than assumptions or anecdotal evidence.
Moreover, professionals are privy to the latest research and treatment modalities, making them invaluable allies in the pursuit of optimal health. They can interpret scientific data and translate it into practical recommendations tailored to individual needs. Their expertise ensures that the strategies employed are not only effective but also align with a person’s overall health profile and any concurrent conditions or medications.
Tailoring a DHT Blocking Strategy
Once an accurate diagnosis has been made, the next step is to devise a comprehensive DHT blocking strategy that is personalized to the individual’s unique biological and lifestyle needs. This is where professional consultation becomes indispensable. A one-size-fits-all approach is rarely effective in hormone regulation, as individual responses to treatment can vary significantly due to genetic, metabolic, and environmental factors.
Professionals leverage their expertise to tailor interventions that may include lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, supplements, or prescription medications aimed at reducing DHT levels. For instance, they may recommend a diet rich in foods that can naturally inhibit DHT production, such as those high in zinc and lycopene. Additionally, they can guide the selective use of natural supplements like saw palmetto or pygeum, which are known for their potential to support hormonal balance.
When medication is required, healthcare professionals can prescribe and monitor FDA-approved treatments, ensuring that they are used safely and effectively. This monitoring is crucial, as improper use of such medications can lead to unwanted side effects or interactions with other drugs.
Ultimately, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional when tailoring a DHT blocking strategy not only enhances the likelihood of achieving the desired health outcomes but also ensures that the journey toward hormonal balance is both informed and safe. By leveraging professional insight, individuals gain a partner in health who is committed to navigating the complexities of hormone regulation with precision and care.
Frequently Asked Questions

- Does blocking DHT regrow hair?
Blocking DHT (dihydrotestosterone) can potentially regrow hair by preventing the miniaturization of hair follicles, particularly in cases of androgenetic alopecia. While individual results vary, many people experience slowed hair loss and some degree of regrowth when using DHT blockers.
- Is egg a DHT blocker?
Eggs themselves are not recognized as direct DHT blockers. However, they are rich in nutrients, such as biotin and protein, that support overall hair health, which can be beneficial in a comprehensive hair care regimen.
- What reduces DHT the most?
Finasteride and dutasteride are pharmaceutical medications that are known to significantly reduce DHT levels. Natural compounds like saw palmetto and pumpkin seed oil are also popular alternatives, though they may not be as potent as pharmaceutical options.
- How do DHT blockers affect hair follicles?
DHT blockers help prevent the miniaturization of hair follicles, leading to thicker hair strands and potentially stimulating regrowth. They maintain the health of hair follicles by reducing the impact of DHT on hair density and growth cycles.
- When should I start using DHT blockers for hair loss?
It’s typically advisable to start using DHT blockers at the early stages of hair thinning or hair loss. Consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist can help determine the most appropriate timing and treatment plan based on individual conditions and patterns of hair loss.
- How long does it take to see results from DHT blocking medications?
Results from DHT blocking medications like finasteride can usually be observed after 3 to 6 months of consistent use. However, visible changes in hair density and regrowth may take up to a year. Continued use is often necessary to maintain results.
| PIN it for later! | ||
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |